A set or assemblage of things connected, associated, or interdependent, so as to form a complex unity; a whole composed of parts in orderly arrangement according to some scheme or plan. - Oxford English DictionaryThe Earth system is composed of interacting physical, chemical, and biological processes that move and change materials and energy on Earth. The system provides the conditions necessary for life.
For example, plants, which are part of the living system, use light energy to change carbon dioxide into organic carbon. Less carbon dioxide in the atmosphere helps to cool Earth. Winds and ocean currents move heat from the tropics to higher latitudes, helping to warm the higher latitudes.
These interconnections are not in a linear motion where it leads from one process to another process systematically. However, if we look at the big picture, we can see that they are connected and interdependent on many other things. (Let's just say that if we were to include everything, it would look very complicated because of numerous arrows).
CARBON CYCLE AND NITROGEN CYCLE
SUN'S EFFECT ON EARTH
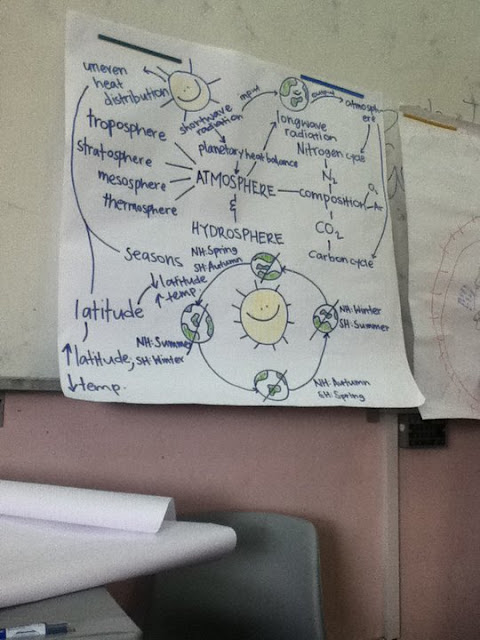
The Sun warms our planet, heating the surfaec, oceans and atmosphere. This energy transferred to the atmosphere drives our weather (found in Stratosphere). Our climate is also strongly affected by the amount of solar radiation received at Earth. This is based on the Earth's albedo.
CLIMATE AND GLOBAL CHANGE
Earth is warm near the equator and cold at the poles, thus it can support a variety of living things because of its diverse regional climates. The avergae of these regions make up Earth's global climate. Climate has cooled and warmed throughout Earth's history for many reasons. The scientific reason is due to the addition of heat-trapping greenhouse gases which are increasing dramatically in the atmosphere as a result of human activities.
Human activities such as Industrial plants, power plants and vehicles with internal combustion engines produce nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Some of these gases are greenhouses gases, meaning that they retain heat in the Earth's atmosphere.
Permafrost is ground that is below the freezing point of water (0°C or 32°F) for two or more years. It is found at high latitudes like the Artic and Antartic. It is also common at high altitudes - like mountainous areas. Permafrost has been thawing relatively quickly in recent years. Scientists have found that the rate of permafrost thaw has increased because of global warming.
RESOURCES
Posted by : Jaspreet Kaur



The images that Jaspreet has attached with regards to the Carbon and Nitrogen cycle enables me to understand the 2 cycles easily. Besides Permafrost, Jaspreet could also give us more examples, such as weather patterns.
ReplyDeleteNur Shahanaz :)